
|
APIs, concepts, guides, and more
|

|
APIs, concepts, guides, and more
|
| void MoveRelative | ( | double | relativePosition, |
| double | vel, | ||
| double | accel, | ||
| double | decel, | ||
| double | jerkPct, | ||
| double | finalVel ) |
MoveRelative with a final velocity. Command a relative point-to-point S-Curve motion.
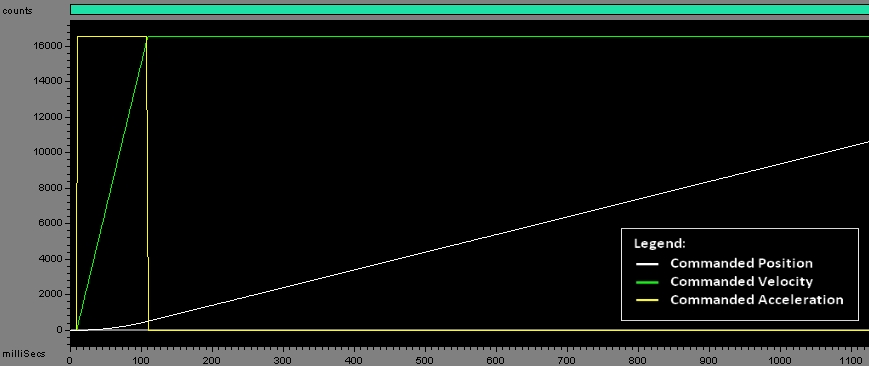
| relativePosition | A relative increment, positive or negative. |
| vel | Maximum velocity, UserUnits/second. |
| accel | Maximum acceleration , UserUnits/second/second. (peak up to 2× accel when jerkPercent = 100, see below) |
| decel | Maximum deceleration , UserUnits/second/second. (peak up to 2× decel when jerkPercent = 100, see below) |
| jerkPct | Jerk Percent, which defines the percentage of acceleration time which is smoothed, 0.0 to 100.0 . |
Using a non-zero JerkPercent increases the maximum acceleration above the user-specified average. If your system can’t handle the higher peak, you risk overshoot or excessive load. The relation between average acceleration and maximum acceleration is:
\[ Maximum Acceleration \;=\; \frac{accel}{1 - \bigl(jerkPercent \times 0.005\bigr)} \]
See the S-Curve Motion concept page for more information.
Using a non-zero JerkPercent increases the maximum deceleration above the user-specified average. If your system can’t handle the higher peak, you risk overshoot or excessive load. The relation between average deceleration and maximum deceleration is:
\[ Maximum Deceleration \;=\; \frac{decel}{1 - \bigl(jerkPercent \times 0.005\bigr)} \]
See the S-Curve Motion concept page for more information.
Part of the Motion method group. See the S-Curve Motion concept page for more information.
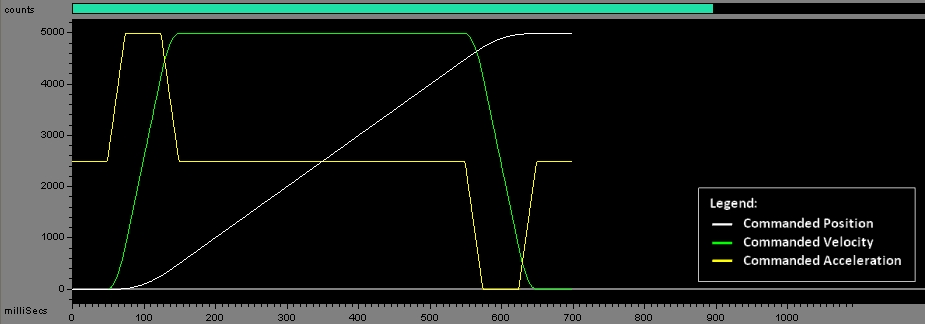
| finalVel | Velocity the Axis will follow after completing the rest of the profile. |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.