The Node Page displays information about your node and allows you to read and write memory values through SDOs.
.png) Node Screen
Node Screen
🔹 Node Info
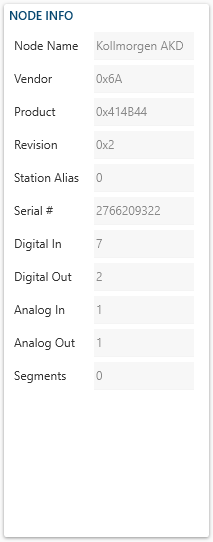
- Node Name displays the name of your node. (A node can be a Drive/Inverter or an IO Block)
- Vendor displays the vendor ID specified in the manufacturer's ESI file.
- Product displays the product ID specified in the manufacturer's ESI file.
- Revision displays the revision number specified in the manufacturer's ESI file.
- Station Alias The EtherCAT station alias.
- Serial # represents your nodes' uniquely identifiable ID. Every node will have a different Serial #.
- Digital In displays the number of Digital Inputs your node contains.
- Digital Out displays the number of Digital Outputs your node contains.
- Analog In displays the number of Analog Inputs your node contains.
- Analog Out displays the number of Digital Outputs your node contains.
- Segments The number of segments on this node.
🔹 SDO Read
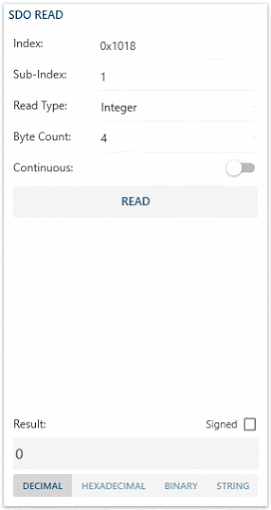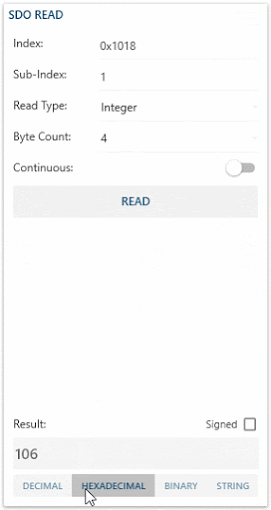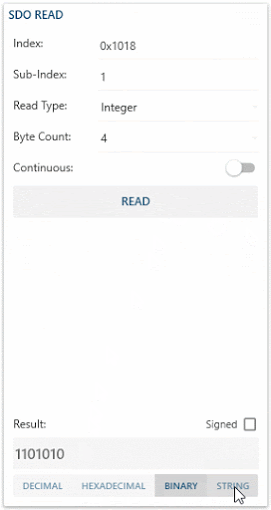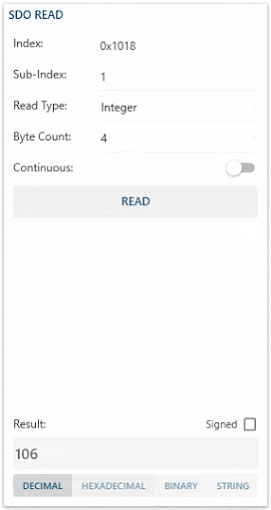
- Index is used to address an entry within the object dictionary. Indexes can represent a single object (variable) or multiple objects (an array or record).
- Sub-Index is used to access individual elements of an object dictionary entry/index.
- For single object dictionary entries such as an Unsigned8, Boolean, Integer32, etc. the value for the sub-index is always zero.
- For complex object dictionary entries such as arrays or records with multiple data fields the sub-index refers to fields within a data-structure pointed to by the main index. Index counting starts with one.
- Read Type allows to specify how you want to insert your Byte Count. As an Integer or as a String.
- Byte Count is used to specify the size of the object dictionary entry/index.
- Continuous Toggle-Button allows you to read the specified index periodically. (No need to press Read button)
- Read Button allows you to read the specified Index.
- Signed CheckBox allows you to display the result as a signed value instead of an unsigned value.
- Result Field displays the read specified Index value.
- Dec-Hex-Bin-Str ListBox allows you to change the way your result value is displayed.
🔹 SDO Write
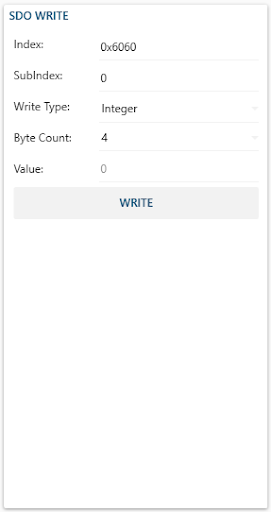
- Index is used to address an entry within the object dictionary. Indexes can represent a single object (variable) or multiple objects (an array or record).
- Sub-Index is used to access individual elements of an object dictionary entry/index.
- For single object dictionary entries such as an Unsigned8, Boolean, Integer32, etc. the value for the sub-index is always zero.
- For complex object dictionary entries such as arrays or records with multiple data fields the sub-index refers to fields within a data-structure pointed to by the main index. Index counting starts with one.
- Read Type allows to specify how you want to insert your Byte Count. As an Integer or as a String.
- Byte Count is used to specify the size of the object dictionary entry/index.
- Value is used to specify the value that will be assigned to the specified Index.
- Write Button allows you to write the specified Value to the specified Index.


.png) Node Screen
Node Screen

